The Gumboro disease context
Gumboro disease or Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) is one of the most widespread viral diseases in poultry production5.
Since the early 90's, the very virulent form of IBD has appeared in West Europe and spread quickly to Central and Easterns Europe, the Middle -East, Asia, South and North America3,4,6.
Very virulent Gumboro causes:
- Acute out breaks with high mortality, up to 70% in layers and 30% in broilers.
- The morbidity rate is very high and could reach 100%.
- Depression, anorexia, ruffled feathers and whitish diarrhoea.
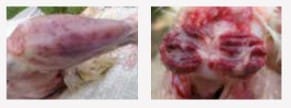
- Bursa de Fabricius is found swollen, gelatinous or haemorrhagic.
- Pectoral and thigh muscles are frequently haemorrhagic.
Classical or subclinical Gumboro causes uneven growth rate and immunosuppression:
- Enhancing the susceptibility to other infections.
- Eliciting a suboptimal immune response to live attenuated vaccines.
- Affecting productive parameters.
Prevention strategy against all forms of Gumboro
Prevention programs including biosecurity must be combined with an efficacious vaccination program.
- The vaccination strategy is based on the selection of attenuated live and inactivated IBDV vaccines for broilers and breeders.
- With the advent of new vaccine technologies, hatchery vaccination is becoming the preferred option for many poultry companies.
- However, for many producers on farm vaccination is still the preferred and suitable solution.
- Thanks to their powerful action, Intermediate Plus vaccines are the only ones able to protect birds with high levels of maternal antibodies.
- Intermediate Plus vaccines have been demonstrated to be the right tool against very virulent Gumboro without impairing the immune response.
1. Ceva's Winterfield 2512, is the original vaccine strain
- It originates form the first case of IBD (Gumboro, Delaware, USA).
- Prof. Winterfield developed the 2512 vaccine strain whilst working at Purdue University and for the company that later became Ceva.
- Scientists at Ceva developed the final product. The method and number of passages is exclusively part of Ceva's know-how. This makes the difference all around the world.
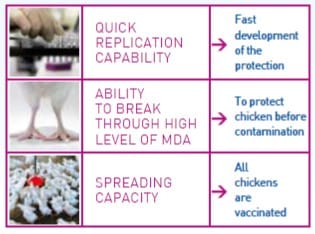
2. Early and strong protection against vvIBD and classical IBD
Cevac IBD 2512 L, is a tool against very virulent and all other forms of Infectious Bursal Disease thanks to:
3. Cevac IBD 2512 L is the solution for drinking water vaccination
- The spreading ability of Cevac IBD 2512 L is an advantage for field vaccination.
- Gumboro virus needs to replicate on lymphoid structures of the gut in order to reach the bursa, this is why it is recommended to give IBD live vaccines through drinking water.
- Vaccination requires professionalism, time and technique. Ceva work on training programs and educational tools with farmers all around the world.
- The use of Cevamune to improve the efficiency of oral vaccination.
4. Efficacy is shown with billions of vaccinated chickens worldwide
Gumboro, Ceva'a expertise.
- Expertise is backed by more than two decades of field presence, hundreds of dedicated people and billions of vaccinated birds.
- Thanks to this knowledge, Ceva produces the widest range of Gumboro vaccines in the market.
- Any live Gumboro vaccine MUST colonise and replicate in the bursa to provide protection. Live vaccines induce mild. transient, and reversible changes in the bursa without any impact on the health of the bird.
- Several studies have shown that Cevac IBD 2512 L will not compromise immune competency. The Newcastle response in SPF birds after 4 days application of Cevac IBD 2512 L was optimal according European Pharmacopoeia protocols2.
- Improved performances and income recorded worldwide after the use of Cevac IBD 2512 L would be impossible in immunocompromised birds.
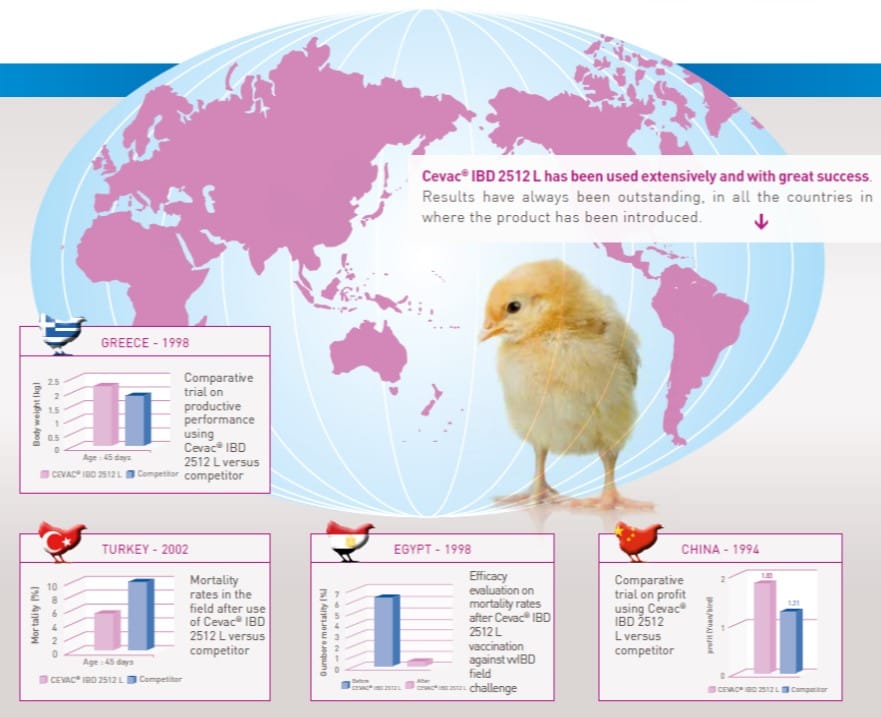
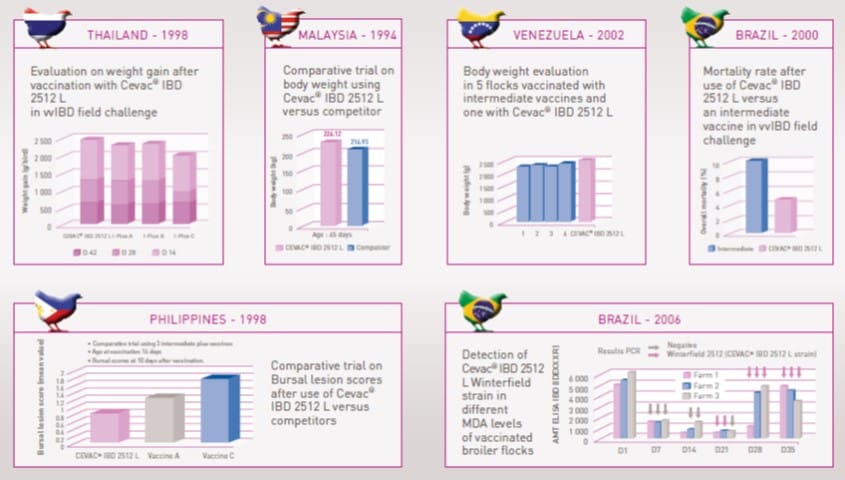
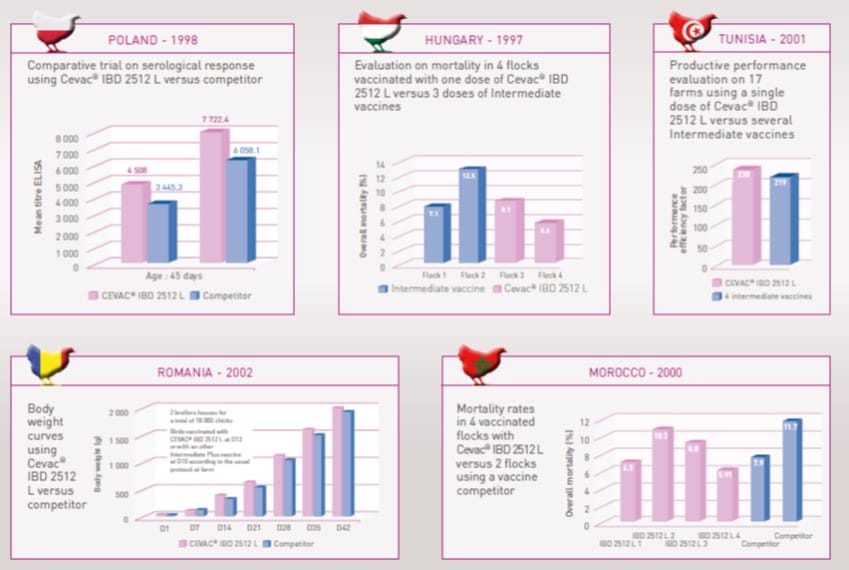
Cevac IBD 2512 L Proven efficacy worldwide7
The reference for field vaccination
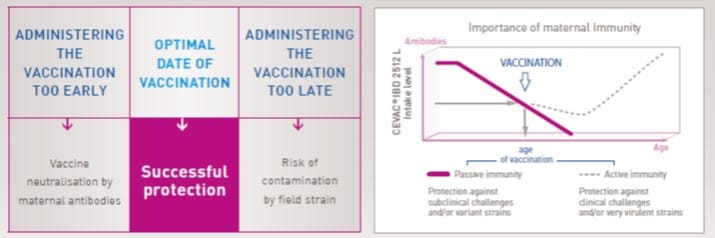
An effective technique at the right time:
- The goal is to protect the chickens by vaccination before contamination by the IBD field virus.
- But chickens can be protected by vaccination only when the vaccine is not neutralised by the maternal antibodies.
- Cevac IBD 2512 L is able to replicate quicker than the field strain and is able to overcome medium and high maternal antibody levels.
References:
1. CEVA Santé Animale. Market Study CEVA Internal Data. 2009. 2. CEVA Santé Animale. Ceva- Phylaxia study DV2/98/22. 1998. 3. DI FABIO J. et al. 1999. European-like pathogenic infectious bursal disease viruses in Brazil. The Veterinary Record, Vol 145 N7. 4. DOMANSKA K. et al. 2004. Antigenic and genetic diversity of early European isolates of Infectious bursal disease virus prior to the emergence of the very virulent viruses: early European epidemiology of Infectious bursal disease virus revisite. Archives of Virology (2004) 149:465-480. 5. LUKERT, P.D; SAIF, Y.M. Infectious Bursal Disease. In: SAIF, Y.M; BARNES, H. J; GLISSON, J. R; FADLY, A. M; MCDOUGALD, L.R; SWAYNE, D. E. (Eds), Diseases of Poultry, 11th Ed. Blackwell Publishing Co. 161-179 pp. 2003. 6. JACKWOOD D. et al. 2009. Characteristics of a Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus from California. Avian Diseases 56:592-600. 7. Data available on request.

 Corporate Website
Corporate Website
 Africa
Africa
 Argentina
Argentina
 Asia
Asia
 Australia
Australia
 Belgium
Belgium
 Brazil
Brazil
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile
Chile
 China
China
 Colombia
Colombia
 Denmark
Denmark
 Egypt
Egypt
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Greece
Greece
 Hungary
Hungary
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Italia
Italia
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Korea
Korea
 Malaysia
Malaysia
 Mexico
Mexico
 Middle East
Middle East
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Peru
Peru
 Philippines
Philippines
 Poland
Poland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Romania
Romania
 Russia
Russia
 South Africa
South Africa
 Spain
Spain
 Sweden
Sweden
 Thailand
Thailand
 Tunisia
Tunisia
 Turkey
Turkey
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 USA
USA
 Vietnam
Vietnam